
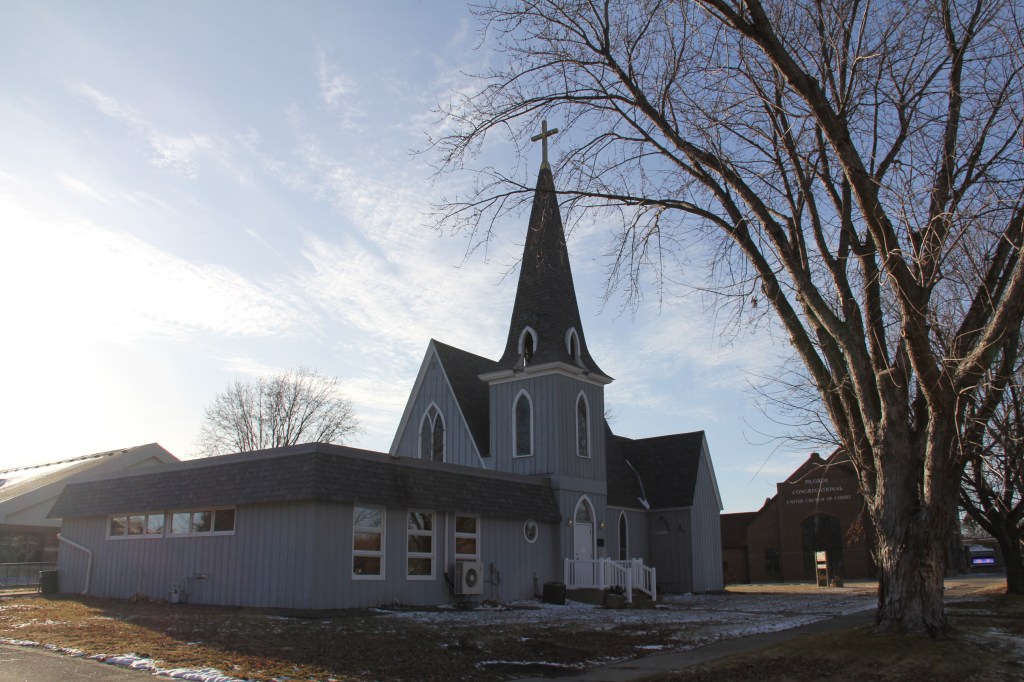
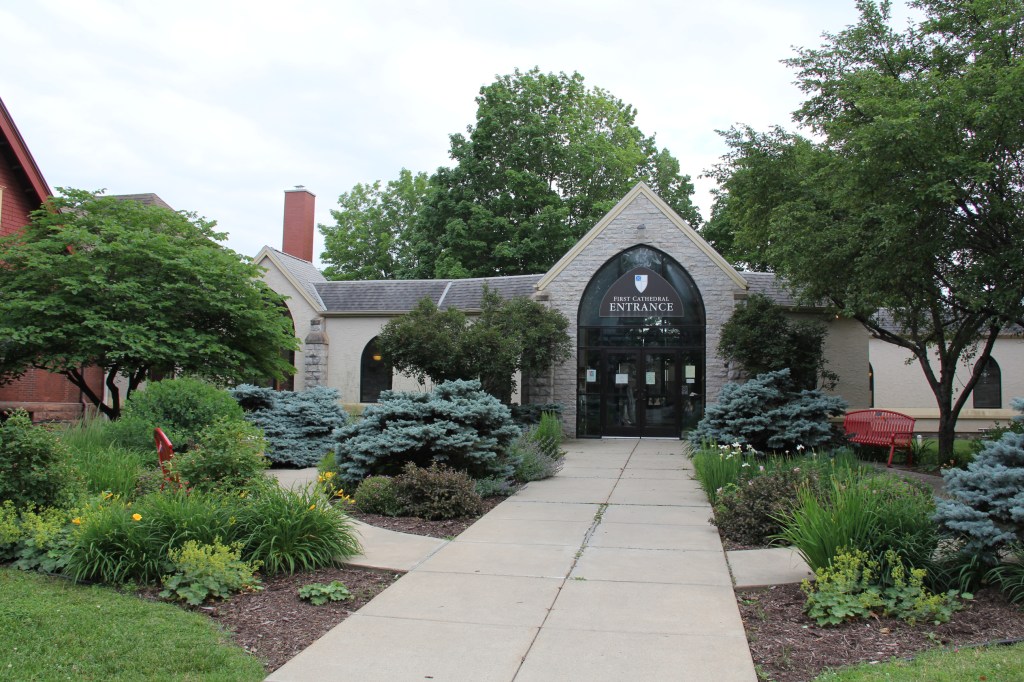
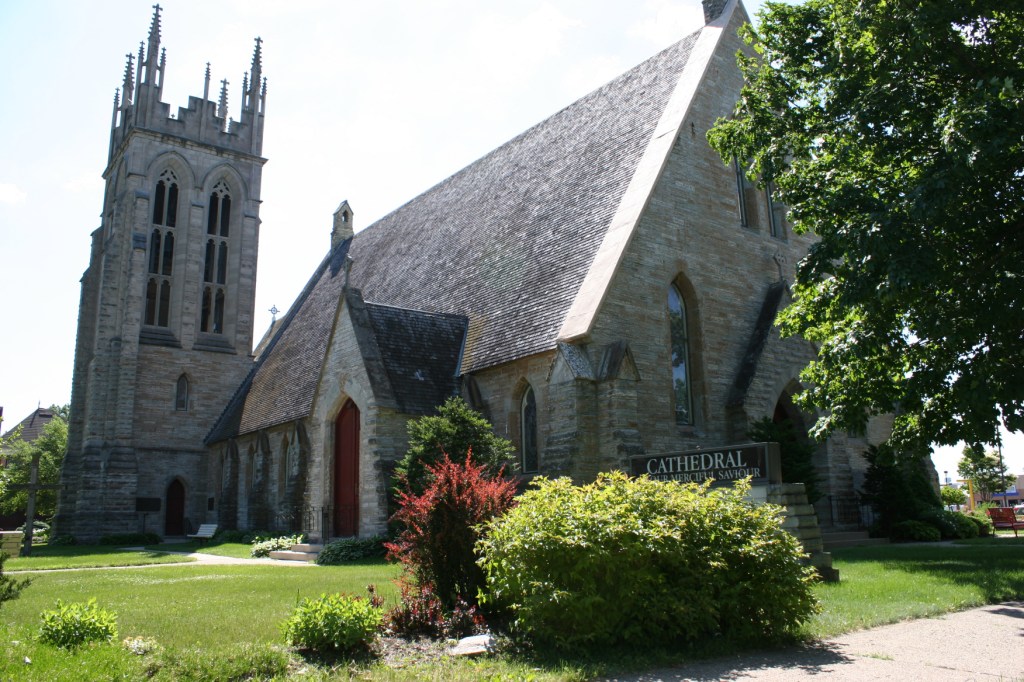
WE GATHERED. On a day when I learned that a friend, an American citizen, was recently racially-profiled and stopped by ICE. On a day when I learned that ICE vehicles have been parked in my neighborhood. On a day when several Minnesota children were released from federal detainment in Texas. On a day when the border czar announced the draw-down of 700 federal agents (out of 3,000) in Minnesota. On this early February day, 75 of us gathered for an “Evening Prayer Service for Our Nation” at the Cathedral of Our Merciful Saviour in Faribault, Bishop Henry Whipple’s church.

I needed this service of prayer, scripture, Psalms, reflection and hymns to quiet my troubled spirit. But I needed, too, to hold space, to sit and stand and sing and pray in community, in support of anyone—especially our immigrant and refugee neighbors—illegally stopped, taken and/or detained by ICE.
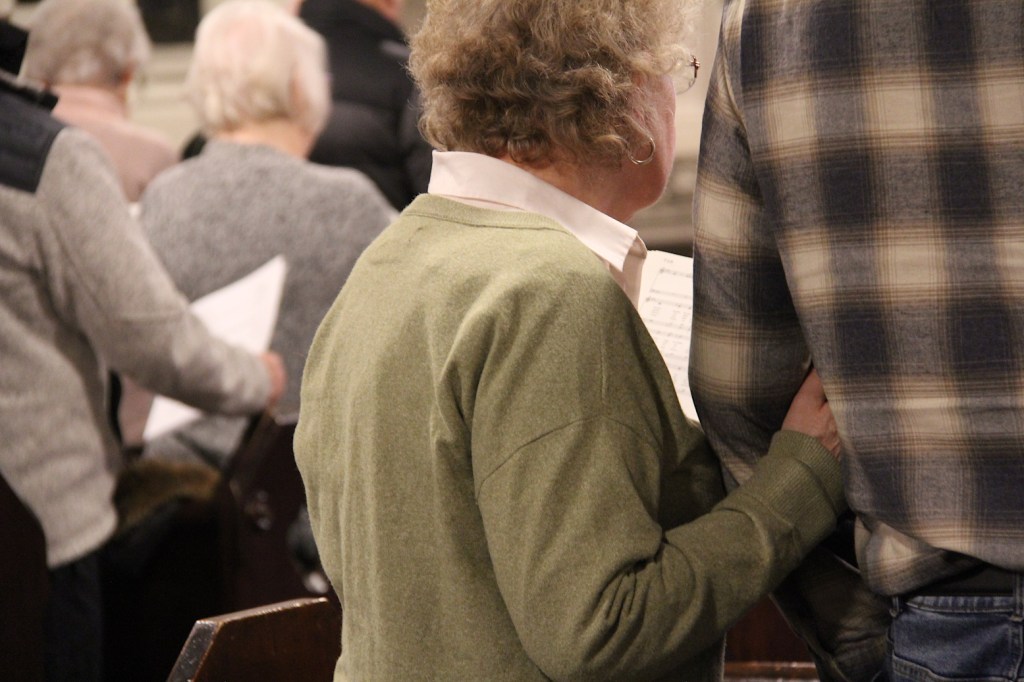
This was not a protest service. Rather, this was a reflective, prayerful, unifying, worshipful coming together of people in my community who care deeply about their neighbors and about this nation.
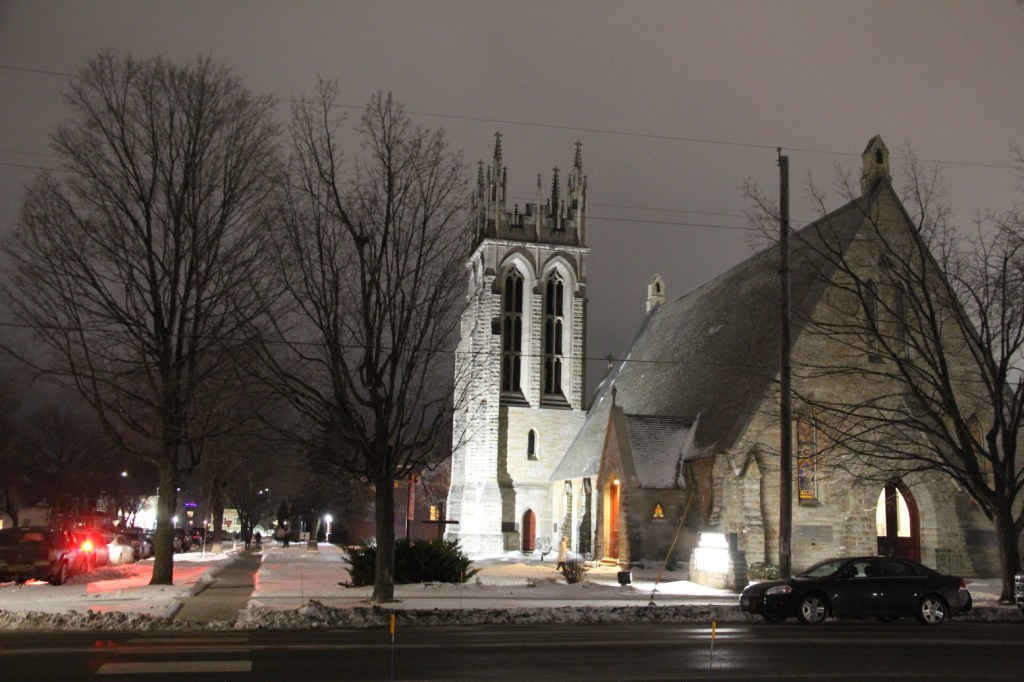
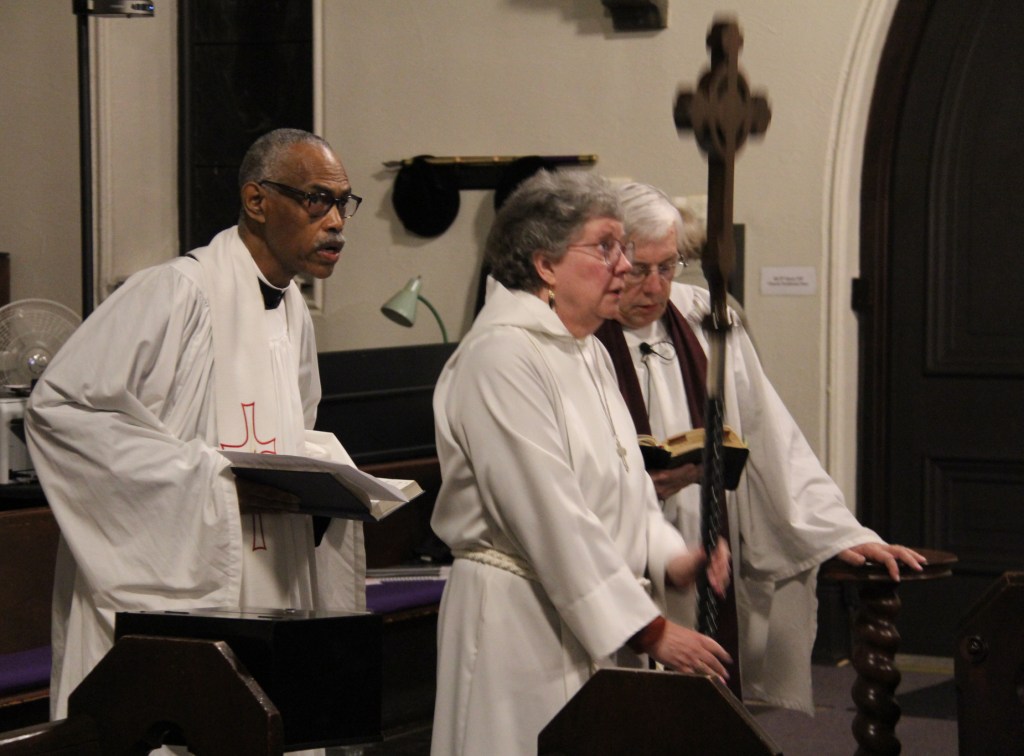
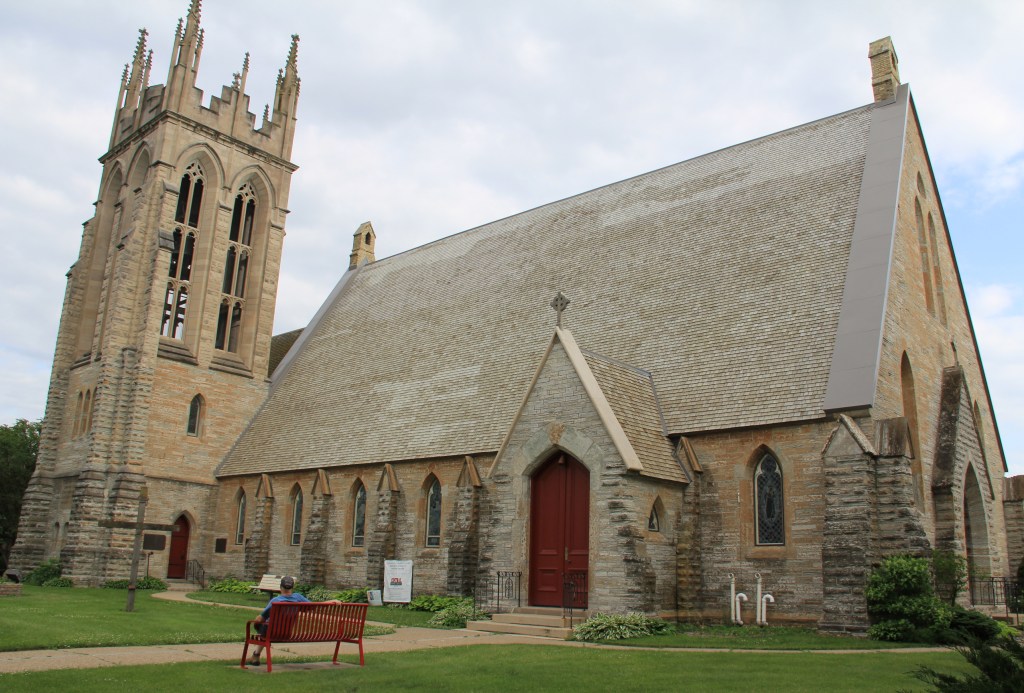
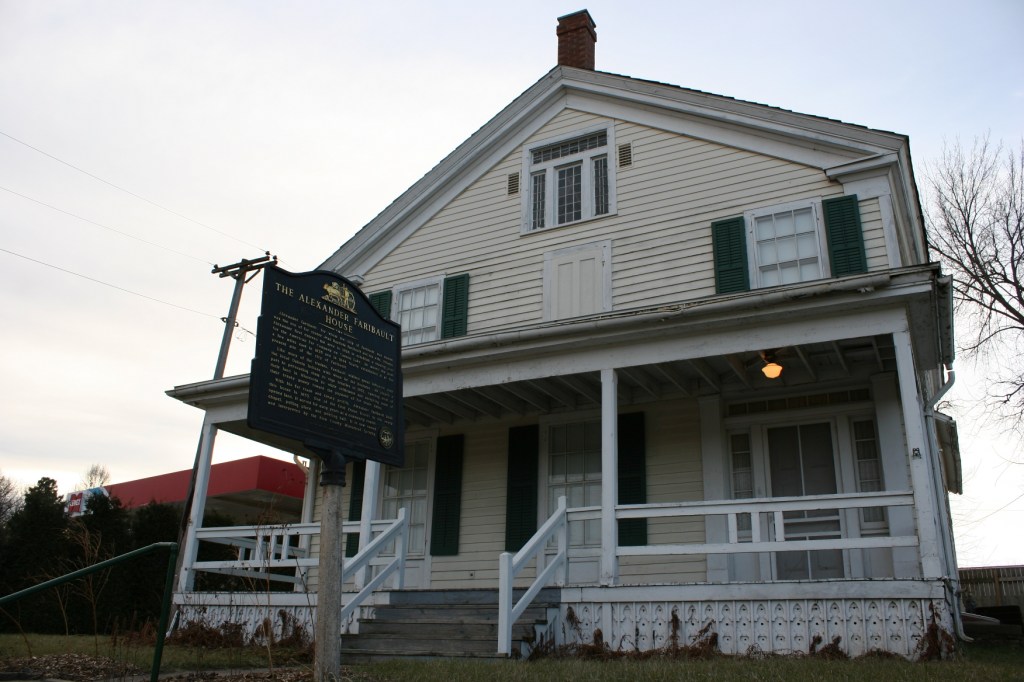
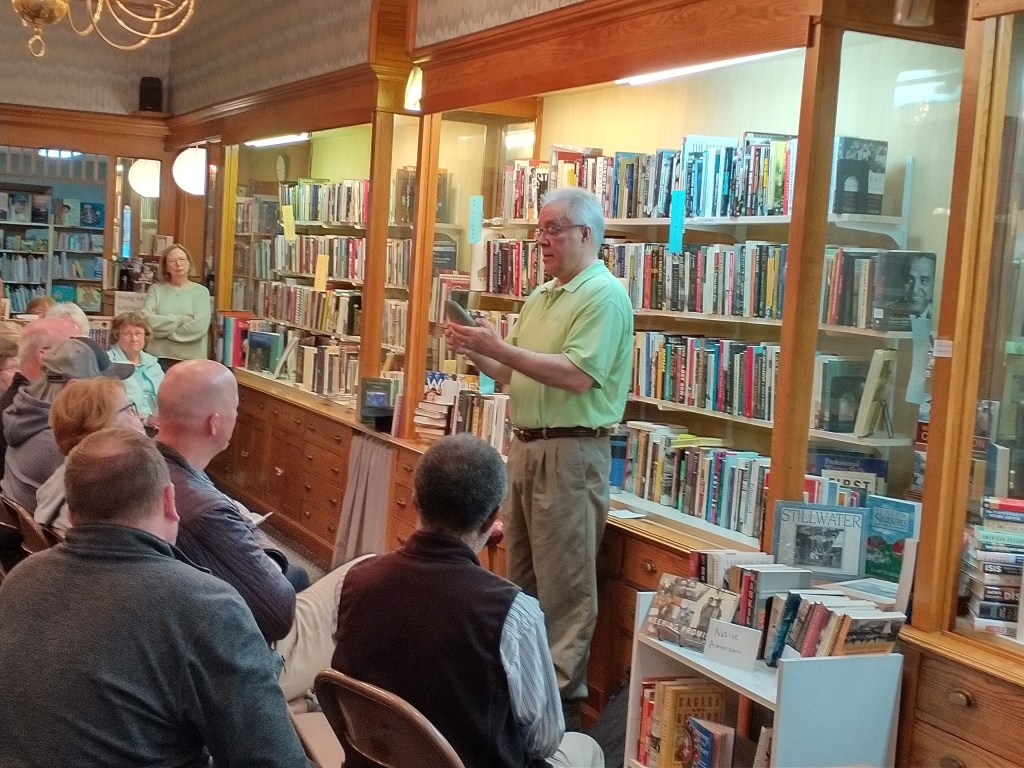
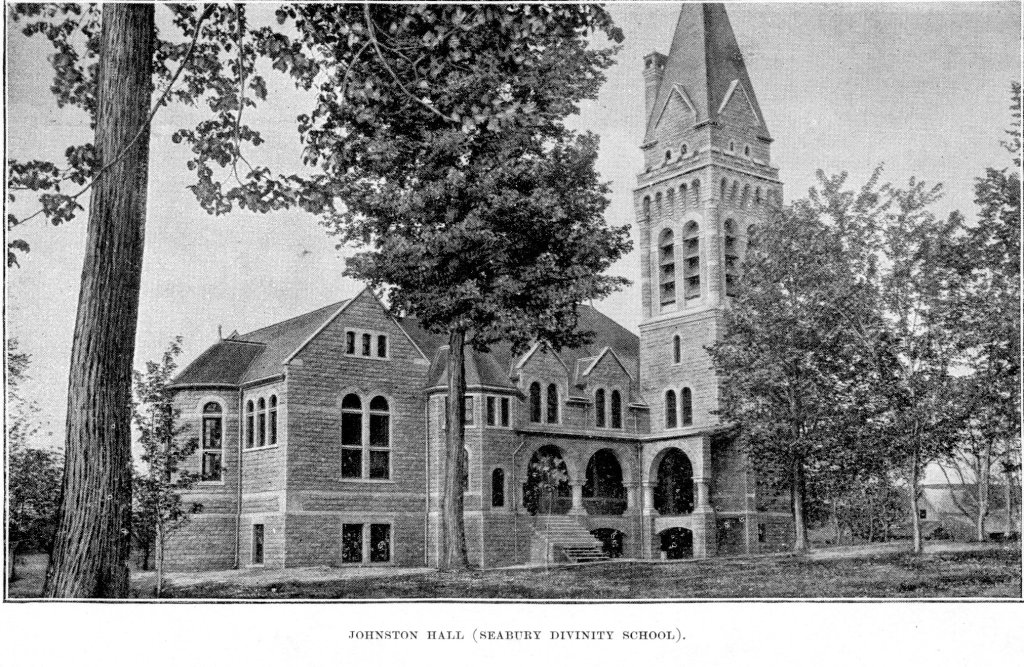
The Rev. James Zotalis welcomed attendees to the event held inside the massive Episcopal cathedral completed in 1869 under the leadership of Bishop Whipple. “Welcome to the Whipple building,” Zotalis said in opening his short homily. “This is the real Whipple building.”
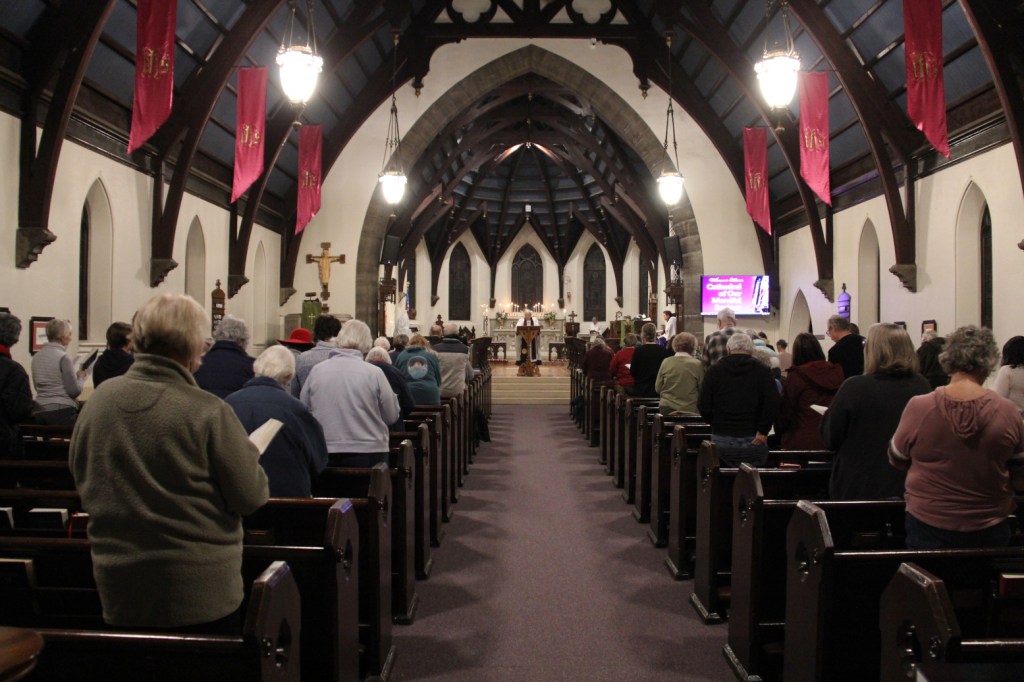

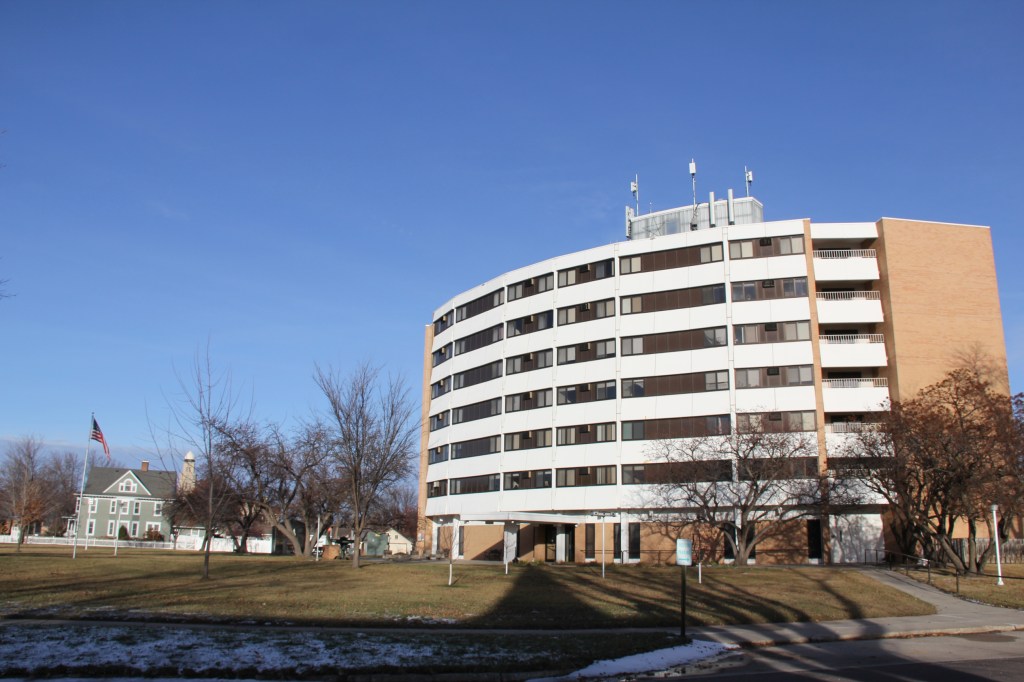
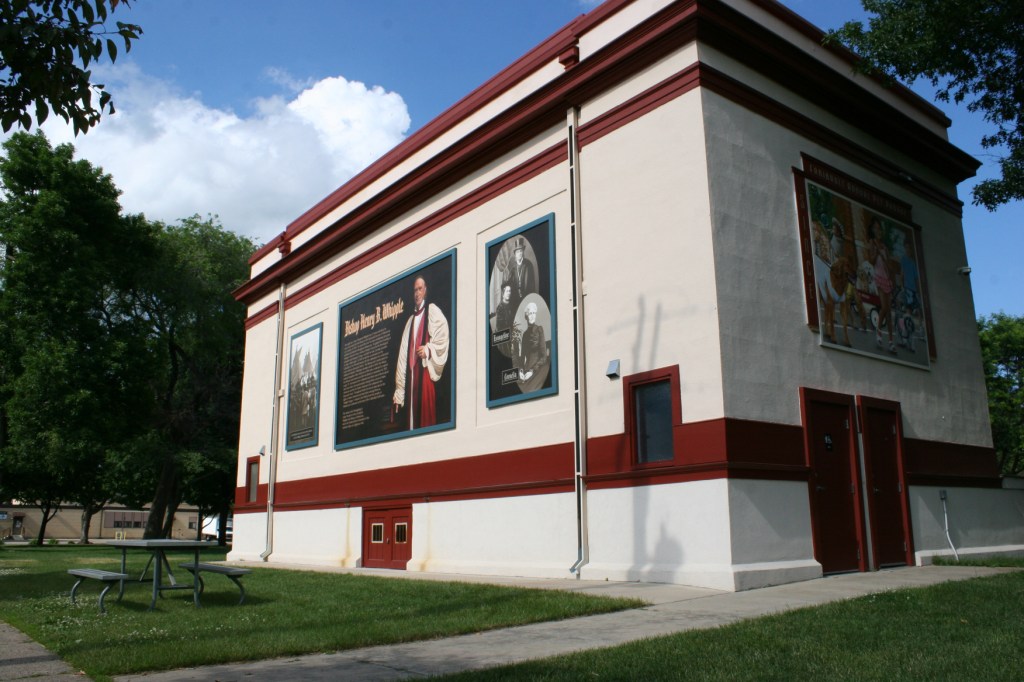
He contrasted the beautiful church to the stark seven-story Whipple Federal Building 50 miles to the north that bears the good bishop’s name and which is now a temporary detention center for those detained by ICE in Minnesota. Conditions inside have been described as “inhumane” by officials who have visited the facility.
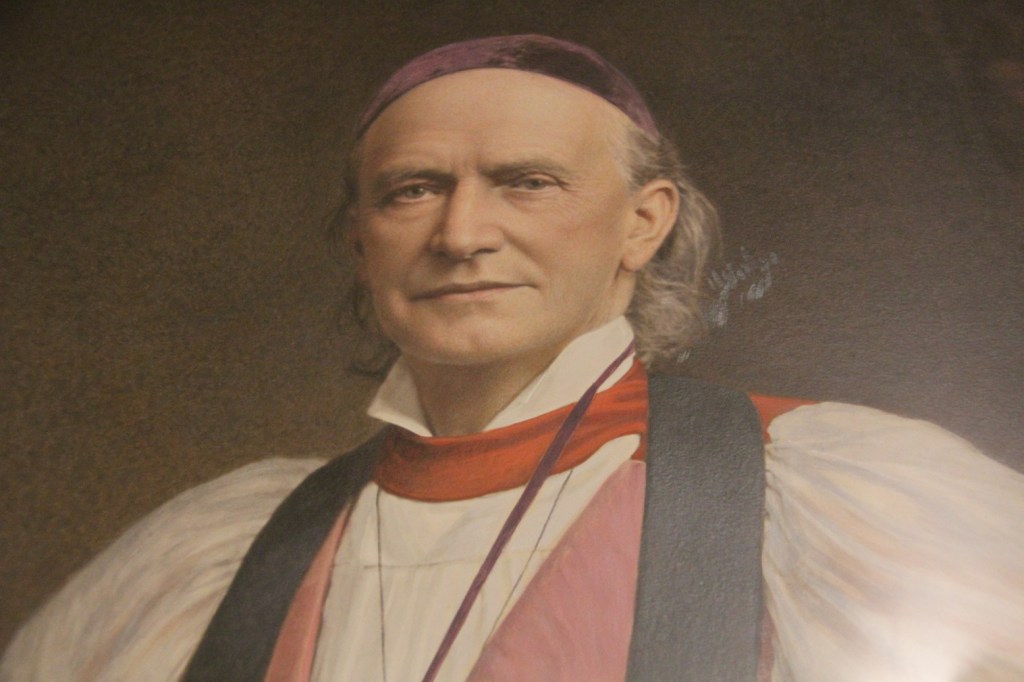

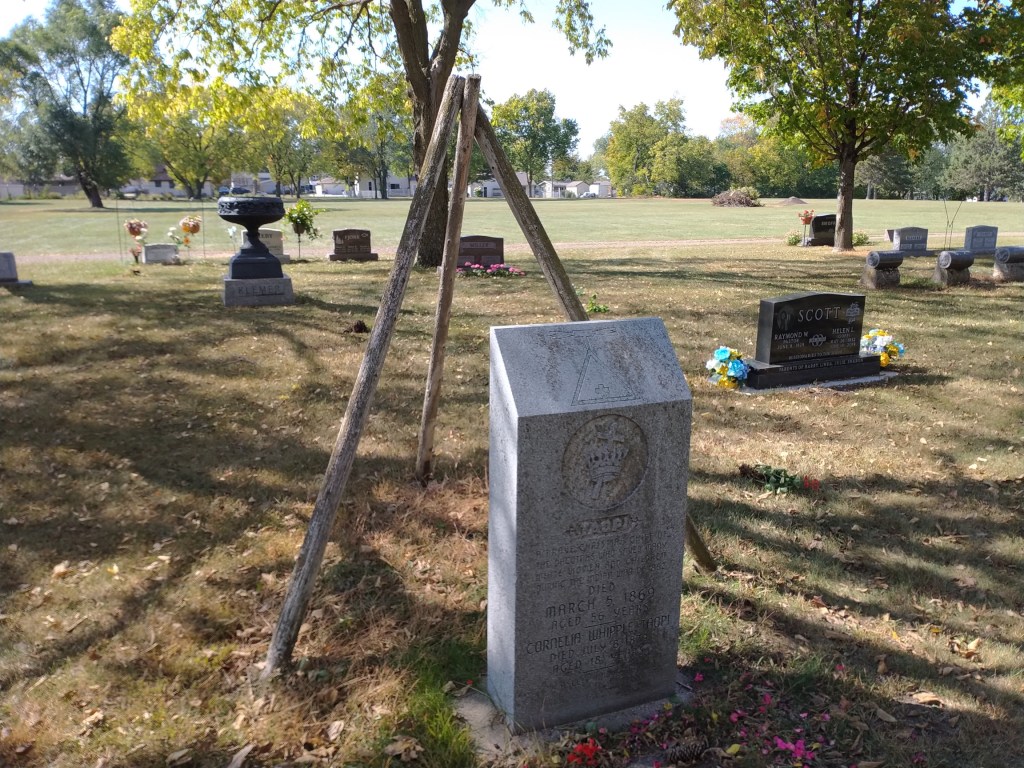
The cathedral, Zotalis said, is a place of love and peace, its ministry modeled after that of Bishop Whipple and his first wife, Cornelia. Arriving here from Chicago in 1859, the couple had already served in dangerous areas of that city, connecting with people in tangible, helpful ways, much like we see Minnesotans stepping up and helping others today.

With a repeated directive to “always say no to evil,” Zotalis said Minnesotans have done just that since the invasion of our state by masked federal agents two months ago. He listed specifics: bringing food to people afraid to leave their homes, providing rides, offering free legal aid and peacefully protesting.

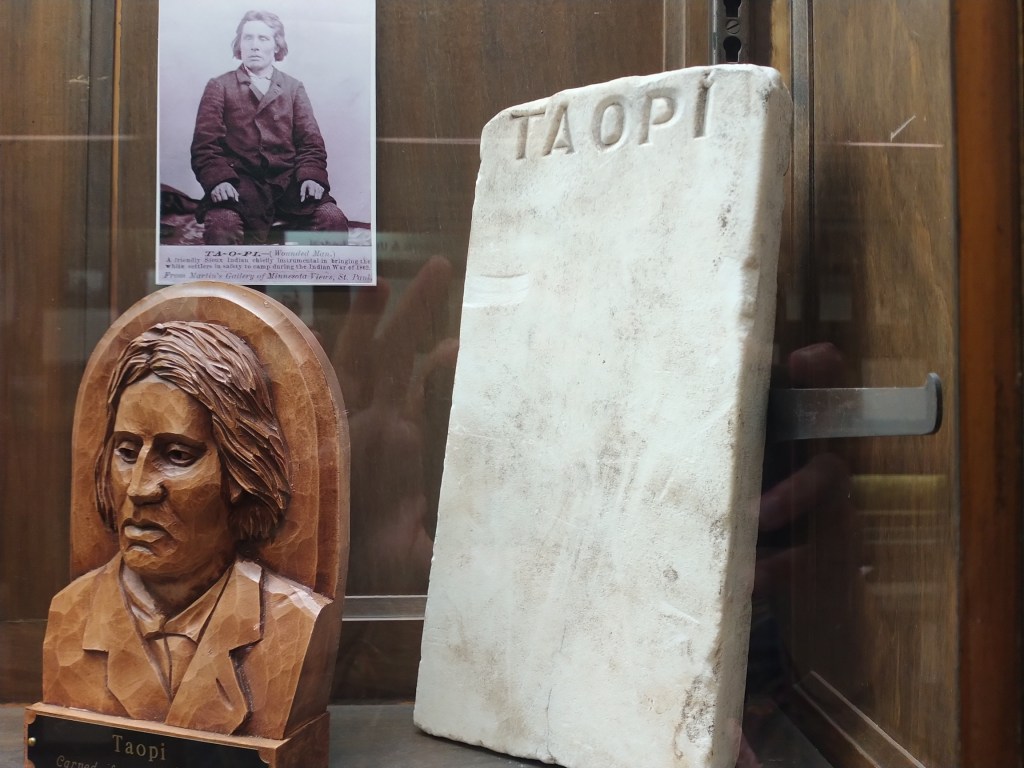
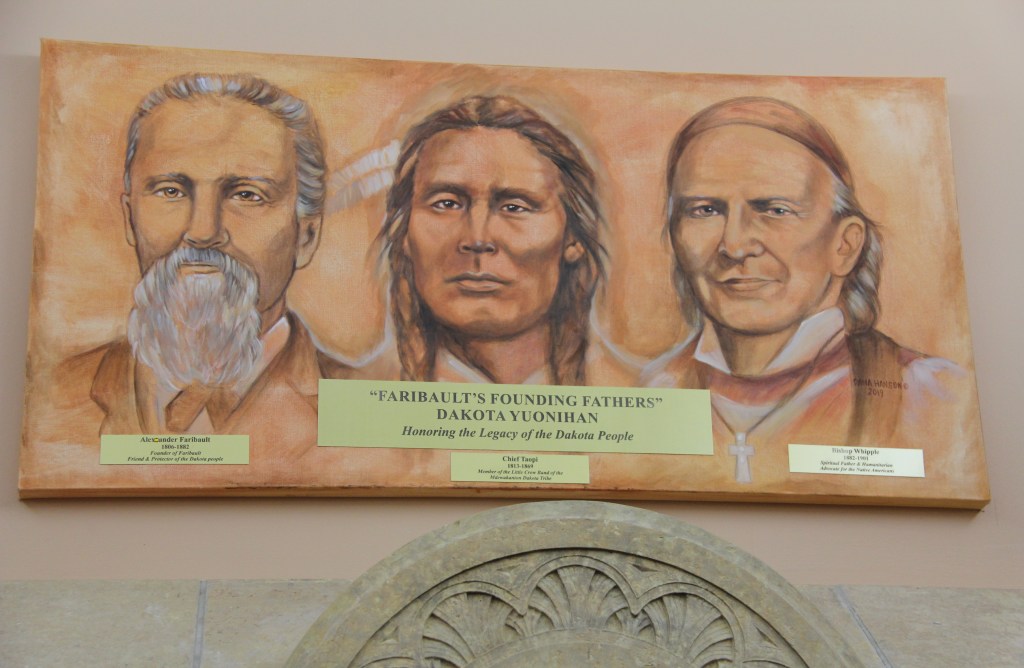
“Love your neighbor as yourself” was emphasized often in love-themed Scripture readings (Luke 10:27, I Corinthians 13:13, I John 4:11) during the Wednesday evening service. Like the good people of Minnesota today, Bishop Whipple showed that love long ago in his ministry to the Dakota people locally, across the state and during their imprisonment after the U.S.-Dakota War of 1862 at Fort Snelling, where the Whipple Federal Building is located. Whipple faced death threats for those who opposed his compassionate work with Native Americans.
Death. In a time of remembrance during Wednesday’s service, attendees could speak the names of “deceased and alive during this time of tragedy and strife.” I spoke first: “Renee Good.” Then another voice: “Alex Pretti.” And then an attendee read the names of 32 individuals who died in ICE detention in 2025. Thirty-two.

Many times my emotions verged on tears. As we asked, “Lord, keep this nation under your care.” As we sang “America the Beautiful.” As we prayed a Collect for Peace. As I thought of Jesus, who also lived in troubled times and who served with love and compassion.
Theme words of love, compassion, mercy and neighbor threaded throughout the service led by the reverends Zotalis and Henry Doyle. I could feel those words. And I could feel, too, the collective sense that we all needed this evening of prayer, scripture, Psalms, reflection and hymns to quiet our troubled spirits.
FYI: To watch a video of the service online, click here.
© Copyright 2026 Audrey Kletscher Helbling
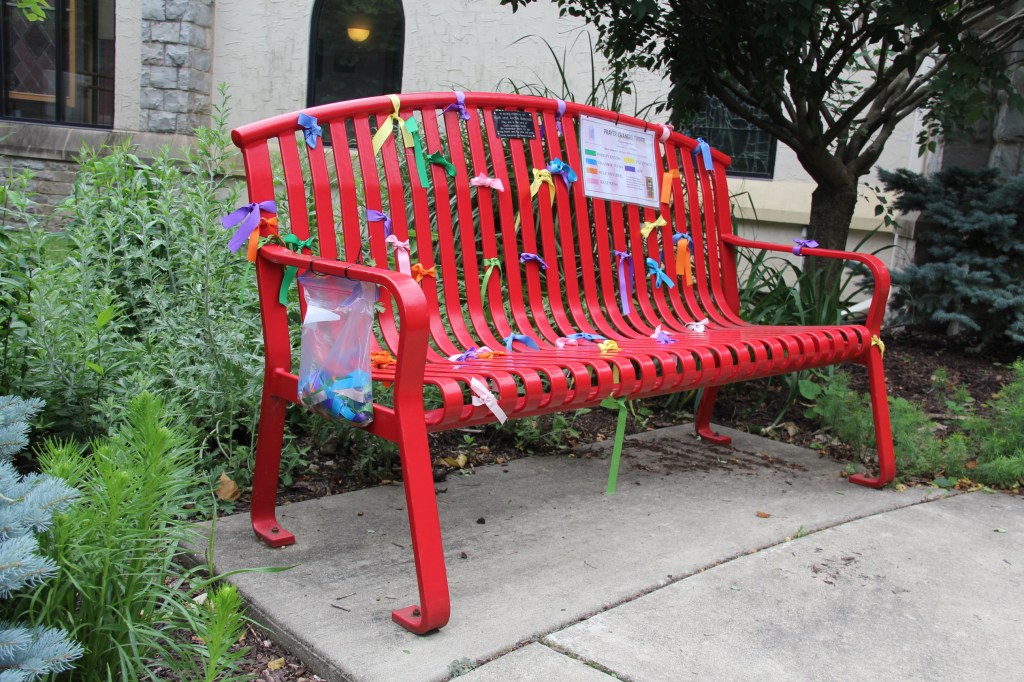
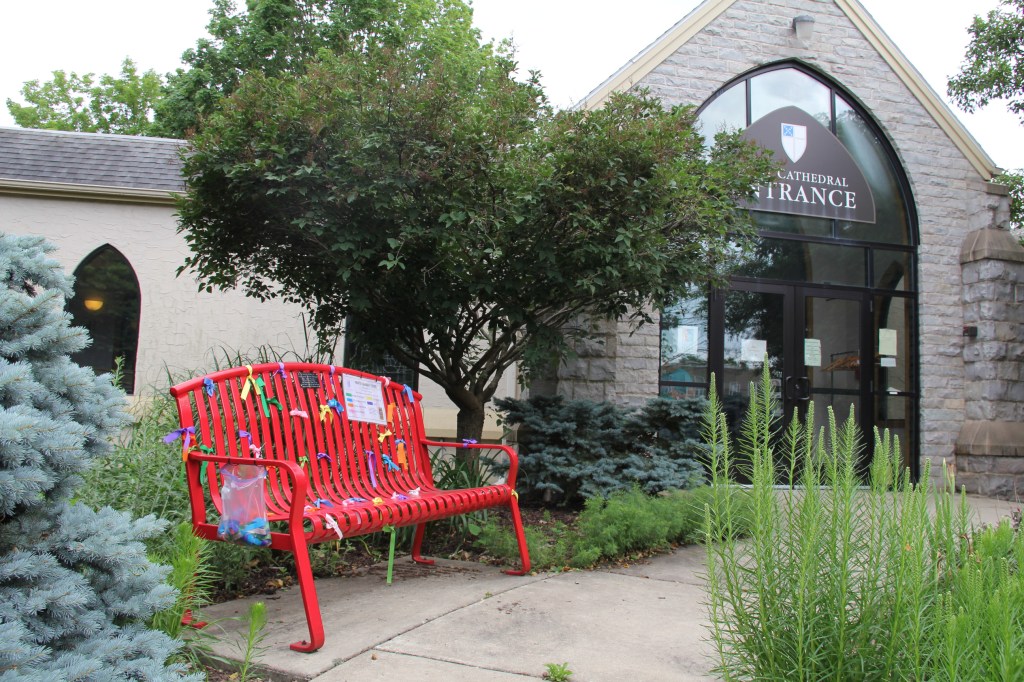









































“Evening Prayer for Our Nation” planned at Bishop Whipple’s church in Faribault February 2, 2026
Tags: "Evening Prayer for Our Nation", America, Bishop Henry Whipple, Bishop Henry Whipple Federal Building, Cathedral of Our Merciful Saviour, commentary, community gathering, faith, Faribault, history, immigrants, Immigration and Customs Enforcement, Minnesota, news, prayer service, refugees, social justice
FIFTY MILES FROM THE NON-DESCRIPT Bishop Henry Whipple Federal Building currently housing ICE detainees in Minneapolis, a beautiful, aged cathedral rises high in the heart of Faribault. Wednesday evening, February 4, that magnificent, massive cathedral—Bishop Whipple’s church—will center a community gathering.
Beginning at 7 p.m. the historic Cathedral of Our Merciful Saviour will open its doors for “Evening Prayer for Our Nation” in support of Faribault’s refugees and immigrants. The Cathedral’s pastor, the Rev. James Zotalis, and the Rev. Henry Doyle will lead the event, which includes prayers, readings, music and teachings from Bishop Whipple.
Organizers also promise networking opportunities and information about ways to help others.
Bishop Whipple, who shepherded this congregation while serving as the first Episcopal bishop of Minnesota beginning in 1859, would surely be pleased with the upcoming gathering just as he would surely be displeased with the imprisonment of detainees at the federal building bearing his name. He would likely be standing alongside protesters protesting immigration enforcement and asking to visit detainees inside.
This clergyman focused his ministry on “justice and mercy for all.” And that is evidenced in his ministry to the Dakota both in Faribault and parts west in Minnesota and then at Fort Snelling. Whipple went to the fort and ministered to the Dakota held captive there following the U.S.-Dakota War of 1862.
When 303 Dakota were sentenced to hanging after the war, Whipple traveled to Washington DC to ask President Abraham Lincoln to spare their lives. Lincoln pardoned most, but 38 were still hung in the nation’s largest mass execution.
If Bishop Whipple was alive today, I expect he would be doing everything in his power to help anyone threatened and/or taken by ICE and CBC. But because he is not here, it is up to us to help. I know many people in my community are helping quietly behind the scenes. Walking kids to bus stops. Giving co-workers rides. Delivering groceries. Donating money and food. Volunteering.
Wednesday evening’s “Evening Prayer for Our Nation” is needed, too. It’s needed to bring people together in community, to unite, to uplift, to pray, to share, to recharge, to publicly support our neighbors, to find tangible ways to help. Bishop Whipple would feel grateful. He cared. And so should we.
#
FYI: Whether you live near or far, Faribault nonprofits are in need of donations to help families sheltering in place during ICE operations in Minnesota. This is not just a Twin Cities metro enforcement. Many communities in greater Minnesota, including mine, are suffering.
Please consider helping immigrants and refugees in my community via a monetary donation to the Community Action Center in Faribault (Community Response Fund) or to St. Vincent de Paul. The need for rental assistance, especially, is growing.
© Copyright 2026 Audrey Kletscher Helbling